Ectopic pregnancy also was known as tubal pregnancy is when the fertilised egg does not attach itself to the womb. It happens in 50 percent of female and is noticeable after first few weeks of pregnancy. This condition may require an emergency medical condition. Learn about ectopic pregnancy and its management in this article below.
What is an Ectopic Pregnancy
In a woman of reproductive age, an egg is released in the fallopian tube every month for fertilisation. The egg stays in the tube for 3-4 days and then heads towards the uterus to get implanted. When egg instead of getting the implant in the womb gets the implant in the fallopian tube or cervix, it is an ectopic pregnancy. In a rare case, the egg gets the implant in ovaries. This pregnancy is not healthy and needs medical attention.
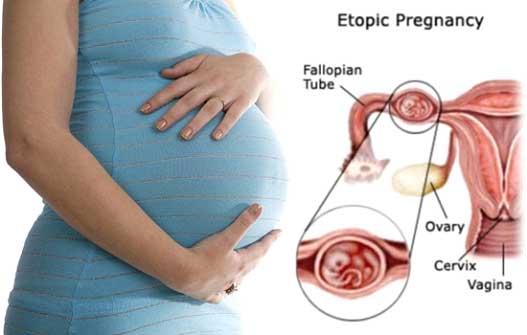
What is an Ectopic Pregnancy
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy happens due to blocked or damaged fallopian tubes, failure in directing the egg to the uterus.
Risk factors for Ectopic Pregnancy
Any women can have an ectopic pregnancy. The common risk factors are sterilising with tubal ligation, prior surgery of fallopian tube or reversal tubal ligation. Pelvic or abdominal surgery may be a reason. Women with previous ectopic pregnancy, with fertility issues, PID, endometriosis, or who is takin DES drugs are more at risk. Alos, women
who get pregnant after 35 years, gets pregnant with IUD is consuming hormonal contraceptive more at the risk or ectopic pregnancy.
What are the Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
In the beginning, there are hardly any symptom. Symptoms start to display between 5th to 14 the week of gestation. Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy include severe and frequent pain in the abdomen. Bright or blood shedding from the vagina. Pain in the shoulder on lying down.

What are the symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
Pain in anus while passing stool. Urge to vomit and diarrhoea. Dizziness. In case you experience any of such symptoms a weeks after gestation do meet your gynaecologist as soon as possible. When a fallopian tube rupture women may feel uneasy, sick and her heartbeat accelerates.
How to Diagnose Ectopic Pregnancy
If you experience pain during first prenatal, your sonographer may suspect an ectopic pregnancy. Ultrasound and blood test are done to confirm. If blood test confirm pregnancy, but the ultrasound shows no embryo in the uterus chances of ectopic pregnancy is very high.
How to Diagnose Ectopic Pregnancy
Mostly is embryo gets attach in the tubes because of the low visibility it may not survive, and sonographer may notice swollen parts, blood clots and resultant tissue. If still nothing is definite, D&C may be done.
Management of Ectopic Pregnancy
The treatment of ectopic pregnancy depends on where the embryo implants. Medicines may be prescribed after determining the complications. Some blood tests may be done following the injection of a drug to check the effectiveness of the drug.
Most of the si=urgeons suggest removal of embryo and repairing of damages. If unsuccessful tubes may be removed if an injury happens.
Home care
After the surgery, the primary aim should be to keep the incision area clean and dry. Check for signs such as unstoppable bleeding, foul smell. Swelling, redness and urge not to touch. Meet your doctor if you experience those symptoms.
Some personal care you need to take are avoided lifting heavyweight, stay hydrated, refrain having sex, do not use tampons, and rest for a couple of weeks.
If you experience an increase in pain notify your doctor immediately.
How to Prevent Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is never preventable. But try to maintain the healthy reproductive system, Make sure your partner wears a condom while having sex. Refrain having multiple sex partners. This measure will prevent STD and PID that causes inflammation and blockage of fallopian tubes.
How to Prevent Ectopic Pregnancy
Make sure visiting your gynaecologist at regular intervals and STD screenings. Do not smoke, exercise regularly and eat healthy and balanced diet. Do not take hormonal contraceptive without consulting your doctor.
Ectopic pregnancy cannot be avoided. If it happens, the embryo needs to remove because of its unhealthy pregnancy. The health of the mother is essential. If she is healthy and her fallopian tube is intact, there is 60 percent chance she will get pregnant in future again.
However, chances of getting pregnant in future depend on the conducted procedure. If medical history is not promising chances of getting pregnant reduces.
No comments:
Post a Comment